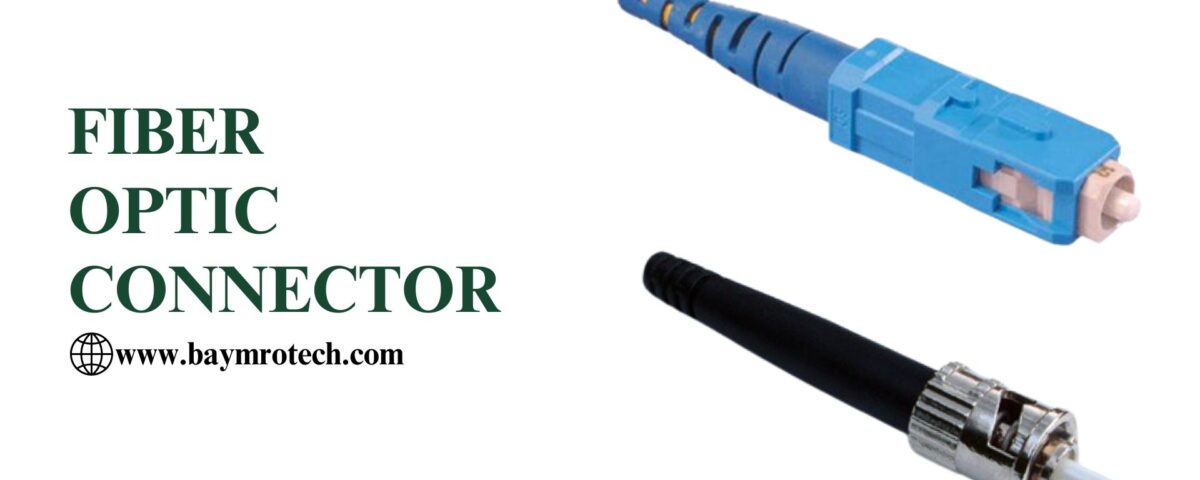
Fiber optic connectors are vital components in optical networks, connecting fiber optic cables to various devices while preserving data integrity and speed. With high-speed data becoming a priority in today’s digital world, these connectors facilitate the smooth transmission of light signals across telecommunications, data centers, and internet infrastructure.
Types of Fiber Optic Connectors:
- SC (Subscriber Connector): Known for its square-shaped design, SC connectors offer a secure, snap-in connection, often used in data centers and large networks.
- LC (Lucent Connector): These connectors are compact, making them ideal for high-density setups. They’re commonly found in high-performance networks where space is at a premium.
- ST (Straight Tip): ST connectors are primarily used in long-distance applications. With their bayonet-style twist-and-lock mechanism, they are popular in commercial and industrial settings.
Benefits of Fiber Optic Connectors:
- High Data Integrity: Fiber optic connectors minimize loss and ensure strong signal retention, supporting high-speed data transfer.
- Durability: Many fiber connectors are designed to withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: Connectors are easy to attach or detach, allowing for quick setups and efficient network changes.


Applications of Fiber Optic Connectors: From telecommunications to healthcare, fiber optic connectors are widely used across industries to connect networking hardware, ensuring fast, reliable data flow in critical settings.
Conclusion: Fiber optic connectors are essential for efficient network performance, supporting the rapid growth in data demands with flexibility, durability, and high performance. Whether in expansive data centers or local area networks, these connectors play a critical role in the connectivity that drives modern communication.