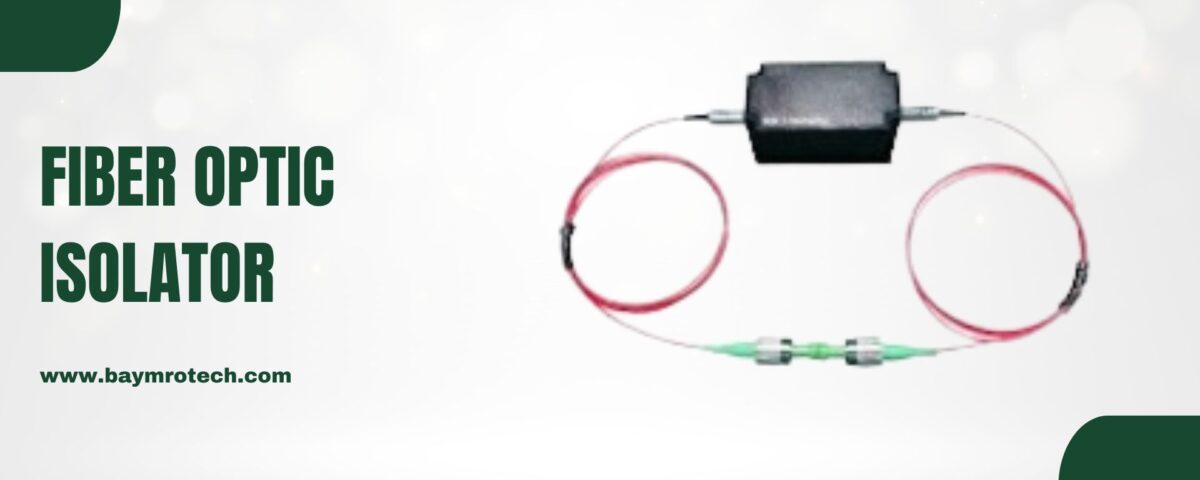
Fiber optic isolators play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and performance of modern optical networks. These passive devices are designed to allow light to pass in only one direction, preventing reflected light from traveling back toward the source. By blocking unwanted reflections, fiber optic isolators help preserve signal quality, improve system stability, and protect sensitive components in communication systems.
How Fiber Optic Isolators Work: Fiber optic isolators use the principles of Faraday rotation to block reflected signals. As light enters the isolator, it passes through a polarization rotator, which alters the orientation of the light wave. This process ensures that any back-reflected light is redirected away from the optical source, preventing interference or potential damage to the system.


Benefits of Using Fiber Optic Isolators:
- Improved Signal Quality: By preventing back reflections, fiber optic isolators help to reduce noise and interference in optical systems, leading to cleaner and more stable signals. This is especially important in high-speed communication networks where even minor signal disruptions can lead to performance issues.
- Protection of Optical Components: Reflected light can cause damage to sensitive components such as lasers and photodetectors. Fiber optic isolators provide essential protection, extending the lifespan of these components and ensuring optimal performance.
- Enhanced Network Stability: In optical amplifiers and other active devices, back reflections can cause oscillations and instability. Fiber optic isolators prevent these issues, contributing to the overall reliability of the network.
Conclusion: Fiber optic isolators are essential for maintaining the quality, stability, and longevity of optical networks. By preventing back reflections, they ensure smoother data transmission and protect critical optical components, making them indispensable in both telecommunications and advanced optical applications.